Preface

An Overview of Competition & Antitrust Regulations and Developments in Africa: 2022
Overview
Status of competition law: geographical overview
Twenty-nine of the 32 surveyed African jurisdictions have national competition law, while only two have no national competition law but are members of a regional competition law body. This is illustrated in the map below:
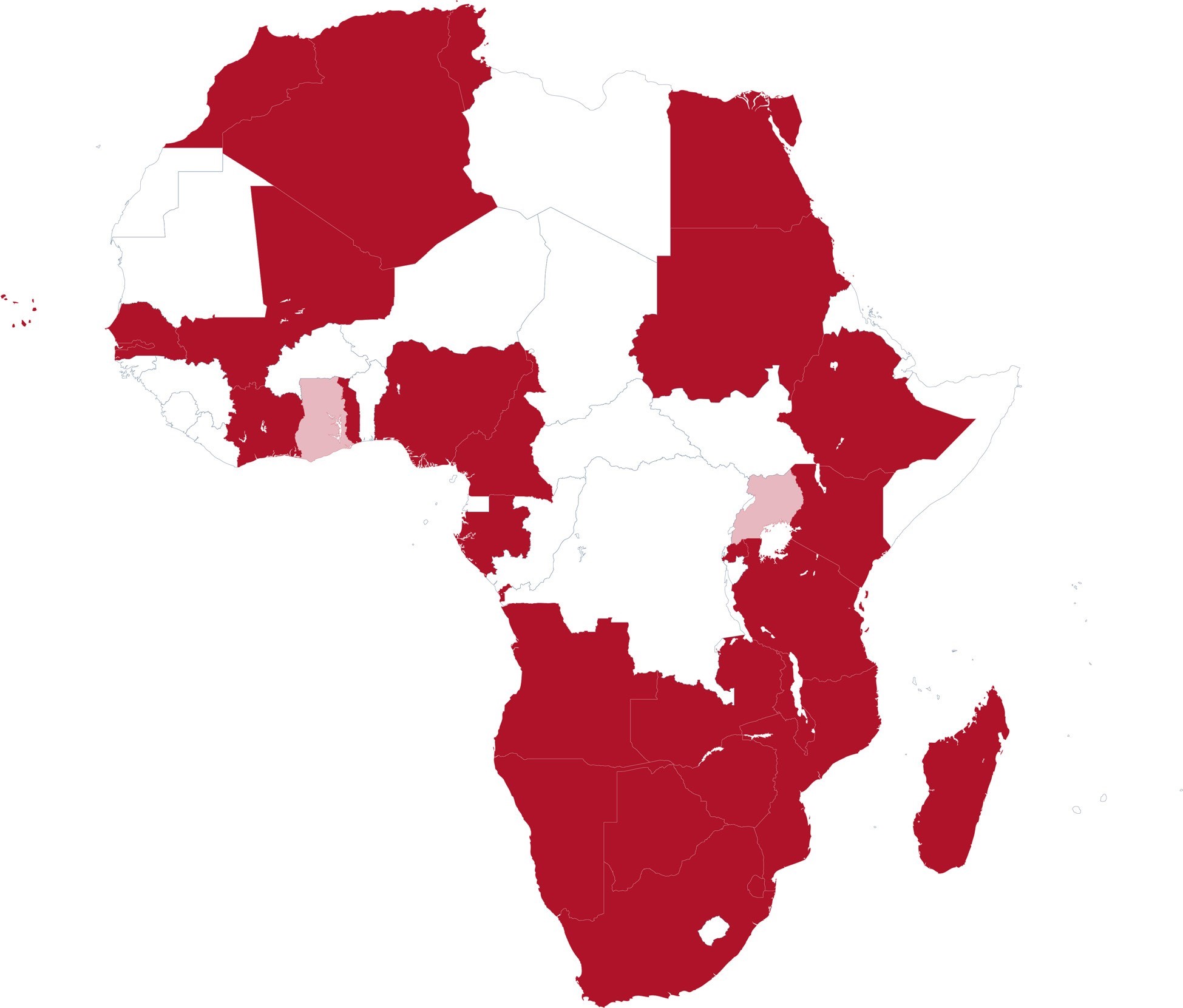
KEY
 Jurisdictions with national competition law
Jurisdictions with national competition law
 Jurisdictions with no national competition law but are part of a regional competition body
Jurisdictions with no national competition law but are part of a regional competition body
|
No. |
JURISDICTION |
DAWN RAIDS |
FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT REGIME |
MERGER FILING |
GUN-JUMPING LAWS |
HORIZONTAL / VERTICAL RESTRAINTS |
|
1. |
Algeria |
No Risk |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Yes |
|
2. |
Angola |
No Risk |
Sector-Specific Laws |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
No |
|
3. |
Botswana |
Low - Medium Risk |
No |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
No |
|
4. |
Cameroon |
No Risk |
Yes |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Yes |
|
5. |
Cape Verde |
No Risk |
Sector-Specific Laws |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
No |
|
6. |
COMESA |
No Risk |
No |
Mandatory & Non- Suspensory |
Yes |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
|
7. |
Cote d’Ivoire |
Low-Medium Risk |
No |
Voluntary & Non- Suspensory |
No |
Yes |
|
8. |
Egypt |
High Risk |
No |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Yes |
|
9. |
Eswatini |
No Risk |
No |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
10. |
Ethiopia |
High Risk |
Yes |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
No |
|
11. |
Gabon |
No Risk |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
12. |
Gambia |
No Risk |
No |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
No |
|
13. |
Ghana |
No risk |
No |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
14. |
Kenya |
Medium Risk |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
|
15. |
Madagascar |
No risk |
Sector-Specific Laws |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
16. |
Malawi |
Medium Risk |
No |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
No |
Yes |
|
17 |
Mali |
No Risk |
No |
Voluntary & Non- Suspensory |
Yes |
No |
|
18. |
Mauritius |
High Risk |
No |
Voluntary & Non- Suspensory |
No |
Yes |
|
19. |
Morocco |
No Risk |
No |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
20. |
Mozambique |
No Risk |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
|
21. |
Namibia |
Low Risk |
No |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
22. |
Nigeria |
High Risk |
Yes |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
23. |
Rwanda |
Low Risk |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
|
24. |
Senegal |
No Risk |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Voluntary & Non- Suspensory |
No |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
|
25. |
South Africa |
Medium - High Risk |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
26. |
Sudan |
No Risk |
Yes |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
No |
|
27. |
Tanzania |
Low Risk |
No |
Voluntary & Non- Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
28. |
Togo |
No Risk |
No |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
No |
No |
|
29. |
Tunisia |
Moderate Risk |
Yes |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Yes |
Yes |
|
30. |
Uganda |
No Risk |
No |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
No |
No |
|
31. |
Zambia |
Low Risk |
No |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
|
32. |
Zimbabwe |
Low Risk |
See Chapter for Further Detail |
Mandatory & Suspensory |
Yes |
Yes |
Notable developments across the region
Over the past two years, African competition regulators have actively engaged in efforts to address these pandemic-related effects, however, there has also been a general upward trend in competition policy enforcement across the continent. A number of African jurisdictions have strengthened their competition and antitrust regimes by way of amendments to existing legislation, the introduction of new laws and regulations, and renewed fervour and political will to enforce existing laws. The notable changes in the surveyed countries are highlighted below:
- Algeria – A new competition legislation is being considered. A first draft of the legislation is currently being reviewed by the Secretariat General of the Prime Ministry.
- Angola – The Competition Regulatory Authority conducted market inquiries on two sectors, namely telecommunications and petroleum products. Merger filing fees were introduced through Executive Decree No. 32/21 of 1 February 2021.
- Botswana – During the 2020/21 financial year, the Competition and Consumer Authority carried out market inquiries (mainly focusing on cartelistic conduct) in the following sectors: abattoirs, construction, waste management, government supplies and animal feed. The Competition and Consumer Authority also expressed concerns in relation to:
- pyramid schemes: the authority has opened an investigation in collaboration with the Botswana Police Service.
- price gouging of essential products during the COVID-19 pandemic: the authority received numerous excessive pricing complaints in relation to basic foods stuffs, healthcare products and hygiene products. The authority cautioned suppliers and has maintained continuous price monitoring in relation to these products.
- vehicle repair garages: during the period July 2021 – September 2021, the authority handled 175 cases concerning the use of sub-standard parts or defective spare parts in vehicles brought in for repair and/or service, resistance of garages to effect warranty terms and unclear pricing practices.
- Cameroon – Cameroon signed a Memorandum of Understanding with the United Kingdom, which sets out the arrangements for applying the effects of the economic partnership agreement from 1 January 2021.
- Cape Verde – Competence on competition matters will be vested on the Ministry of Finance in the short to medium term as there is currently no effective competition regulatory body.
- COMESA – there were various developments in 2021, including the following:
- On 11 February 2021, the COMESA Competition Commission issued a Practice Note in which it amended the interpretation of the term “operate”. Prior to 11 February 2021, a party ‘operated’ in a COMESA Member State if it had turnover or assets in that Member State in excess of USD 5 million. This requirement has now been removed effective 11 February 2021, and a party will ‘operate’ in a COMESA Member State merely if it is active in it (without a minimum turnover or asset threshold). The impact of this will be to make it easier for a transaction to fall within the scope of the COMESA merger control regime.
- The COMESA Competition Commission also issued the following guidelines, namely Draft Guidelines on Fines and Penalties, Draft Guidelines on Settlement Procedures and Draft Guidelines on Hearing Procedures.
- On 6 September 2021, the COMESA Competition Commission issued its first penalty for failure to notify a transaction within the prescribed time periods, which amounted to 0,05% of the parties’ combined turnover in the common market in the 2020 financial year. This was imposed in relation to the proposed acquisition by Helios Towers Limited of the shares of Madagascar Towers SA and Malawi Towers Limited.
- In December 2021, the COMESA Competition Commission imposed a fine for failure to comply with a commitment contained in a merger clearance decision.
- The COMESA Competition Commission conducted eight investigations into restrictive business practices in 2021.
- Egypt – there were numerous developments in Egypt in the past year, including the following:
- On 25 November 2020, the Competition Authority announced that the Egyptian Prime Ministry approved the Prime Minister’s draft law amending certain provisions of the Egyptian Competition Law 3/2005. On 18 February 2021, the Egyptian parliament’s Economic Affairs Committee started the discussions on the new amendments.
- In addition, the Competition Authority has, in the past year, initiated market inquiries in relation to multiple sectors including healthcare, food, electronic and electrical appliances, automotive, real estate, media and petroleum sectors.
- In April 2021, the Economic Court of Cairo issued a ruling in a criminal case brought in March 2020, by the Competition Authority, against five individual poultry brokers for colluding to fix the price of chicken to the detriment of consumers and chicken breeders. The court fined each broker 30 million Egyptian pounds (approx. EUR 1.6 million) for agreeing to fix the price of a kilogram of chicken.
- In July 2021, the Competition Authority initiated a criminal case against two companies who agreed to submit identical offers in one of the practices of the General Authority for Veterinary Services, in violation of Egyptian competition law.
- The head of the Competition Authority announced plans for the creation of an Arab Competition Network (“ACN”) to enhance cross-border cooperation between antitrust enforcers in the Middle East. The ACN would be the first to provide Arab competition authorities with an official platform to meet and discuss prominent issues and impending changes to antitrust law. The network would be run by the 22 members of the League of Arab States, which includes Egypt, Syria, Lebanon, Iraq, Jordan and Saudi Arabia, among others.
- Eswatini – developments in Eswatini include the following:
- The Competition Commission published a Competition Bill, 2020 (Draft Bill), which is intended to be presented to the Minister of Commerce, Industry and Trade. The object of the Draft Bill is to increase effectiveness, consistency, predictability and transparency in the enforcement and administration of competition law in Eswatini. It also aims to give effect to regional frameworks, such as COMESA Competition Regulations and international best practices. The Draft Bill has yet to be signed into law.
- On 20 April 2021, the Competition Commission published guidelines on market definition, which adopt international best practices.
- Ethiopia – The Trade Competition and Consumer Protection Authority is working on regulations to provide guidance on the application of the Trade Competition and Consumer Protection Proclamation (No 813/2013). Proclamation No. 1263/2021, which is expected to be enacted into force in 2022, transfers the powers of the Trade Competition and Consumer Protection Authority to the Ministry of Trade and Regional Integration.
- Gambia – The Ministry of Information is currently reviewing a Merger Commission, which will be effective in maintaining and encouraging competition in markets, to promote and ensure fair and free competition, and to protect the welfare and interests of consumers. The Competition Commission has initiated the following market studies: Hajj Market Study; Rice and Sugar Market Study; Liquefied Petroleum Gas Market Study; Cement Market Study; Tourism Market Study; Banking Market Study; and Vehicle Procurement Market Study.
- Ghana – A draft Competition and Fair Trade Practices Bill is before parliament for consideration.
- Kenya – There have been various recent developments in Kenya, including the following:
- The Competition of Authority finalised its study into the regulated and unregulated credit markets in Kenya and issued its report in May 2021.
- The Competition Authority further developed the Retail Trade Code of Practice 2021, in consultation with stakeholders in the retail sector, to address the abuse of buyer power issues arising from the sector.
- In 2021, the Competition Authority conducted a dawn raid in the steel industry.
- The Competition Authority issued draft joint venture guidelines in 2021, to clarify the rules and filing requirements of joint venture arrangements.
- Malawi – Notable developments in Malawi include the following:
- Amendments to the Competition and Fair Trading Act and the regulations have been proposed and submitted to the Ministry of Justice.
- Furthermore, the Competition and Fair Trading Commission has new drafted new guidelines on various topics, including abuse of dominance and collusive conduct, exclusive dealing arrangements and resale price maintenance, market definition, discriminatory and tying conduct, and public interest, amongst others. These guidelines have been circulated to various stakeholders for comment, but have yet to be published.
- The Competition and Fair Trading Commission recently concluded a market inquiry in the funeral services market, and is currently conducting a market study on digital markets.
- Mauritius – The Competition Commission concluded a market study in the pharmaceutical sector on 8 June 2021.
- Mozambique – There were numerous in Mozambique in 2021, including the following:
- The Competition Regulatory Authority became operational in January 2021.
- Regulations on Merger Notifications Forms were enacted by means of Resolution No. 1/2021 of 22 April 2021. The Regulations prescribe the different forms to be completed for merger notifications, as well as the details of the information and documentation required.
- Regulations on Filing Fees were enacted by means of Ministerial Diploma No. 77/2021 of 16 August 2021. Filing fees are currently set at 0.11% of the turnover of the parties in the previous year, up to a maximum of MZN 2,250,000.
- Amendments to the Competition Regulations were enacted by means of Decree No. 101/2021 of 31 December 2021.
- Namibia – A Competition Bill is in progress and the Competition Commission expects to submit the final version of the Competition Bill to the Ministry of Industrialisation and Trade by the end of June 2022.
- Nigeria – On 2 August 2021, Nigeria adopted the Merger Review (Amended) Regulations 2021, which set out new fees applicable for merger filings. The Federal Competition and Consumer Protection Commission launched and publicised an investigation into the alleged anticompetitive conduct of five companies in the shipping and freight forwarding industry in October 2021.
- South Africa – there were various developments in South Africa in 2021, including the following:
- On 19 May 2021, the Competition Commission launched the Online Intermediation Platforms Market Inquiry, focusing on four broad online intermediation platforms and market dynamics that specifically affect business users, namely: eCommerce marketplaces, online classified marketplaces, software app stores and intermediated services (such as accommodation, travel, transport and food delivery). The inquiry is ongoing with a provisional report scheduled for release in the first half of 2022, and the final report scheduled for release on 4 November 2022.
- On 7 April 2021, the Competition Commission released its market inquiry reports on Land Based Public Transport.
- Furthermore, in April 2021, the Competition Commission published its final report on an impact assessment study it conducted in relation to COVID-19. The report sets out the findings of the Competition Commission regarding the impact of the COVID-19 block exemptions and the enforcement work done by the Competition Commission during the pandemic.
- The Competition Commission’s fifth Essential Food Pricing Monitoring Report, which is released quarterly focused on tracking the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and consequent economic crisis on food markets.
- In November 2021, the Competition Commission released its Economic Concentration Report, which highlights patterns of concentration and participation in the South African economy. The report includes details on the Competition Commission’s power to launch market inquiries into highly concentrated industries, as well as its increased authority to impose structural remedies on businesses in these sectors.
- In May 2021, the Competition Commission issued, for comment, draft guidelines on Small Merger Notifications, which contain specific guidance applicable to the assessment of digital mergers.
- The Competition Commission prohibited a merger solely on public interest grounds, making it the first transaction to be prohibited on non-competitive grounds. Ultimately, however, the merger was conditionally approved before the Competition Tribunal.
- In March 2022, the Competition Commission issued Guidelines on Collaboration between Competitors on Localisation Initiatives, which are aimed at aimed at providing guidance to industry and government on how industry players may collaborate in identifying opportunities for localisation and implementing commitments related to localisation initiatives in a manner that does not raise competition concerns.
- In March 2022, the Competition Commission launched a market inquiry into the South African fresh produce market, which will examine whether there are any features in the fresh produce value chain, which lessen, prevent or distort the competitiveness of the market.
- The Competition Commission concluded various settlement agreements with market players (e.g., grocery retailers, laboratories) to reduce prices of goods and services.
- Zimbabwe – In March 2021, the Competition and Tariff Commission published draft guidelines on Horizontal Agreements for comment.
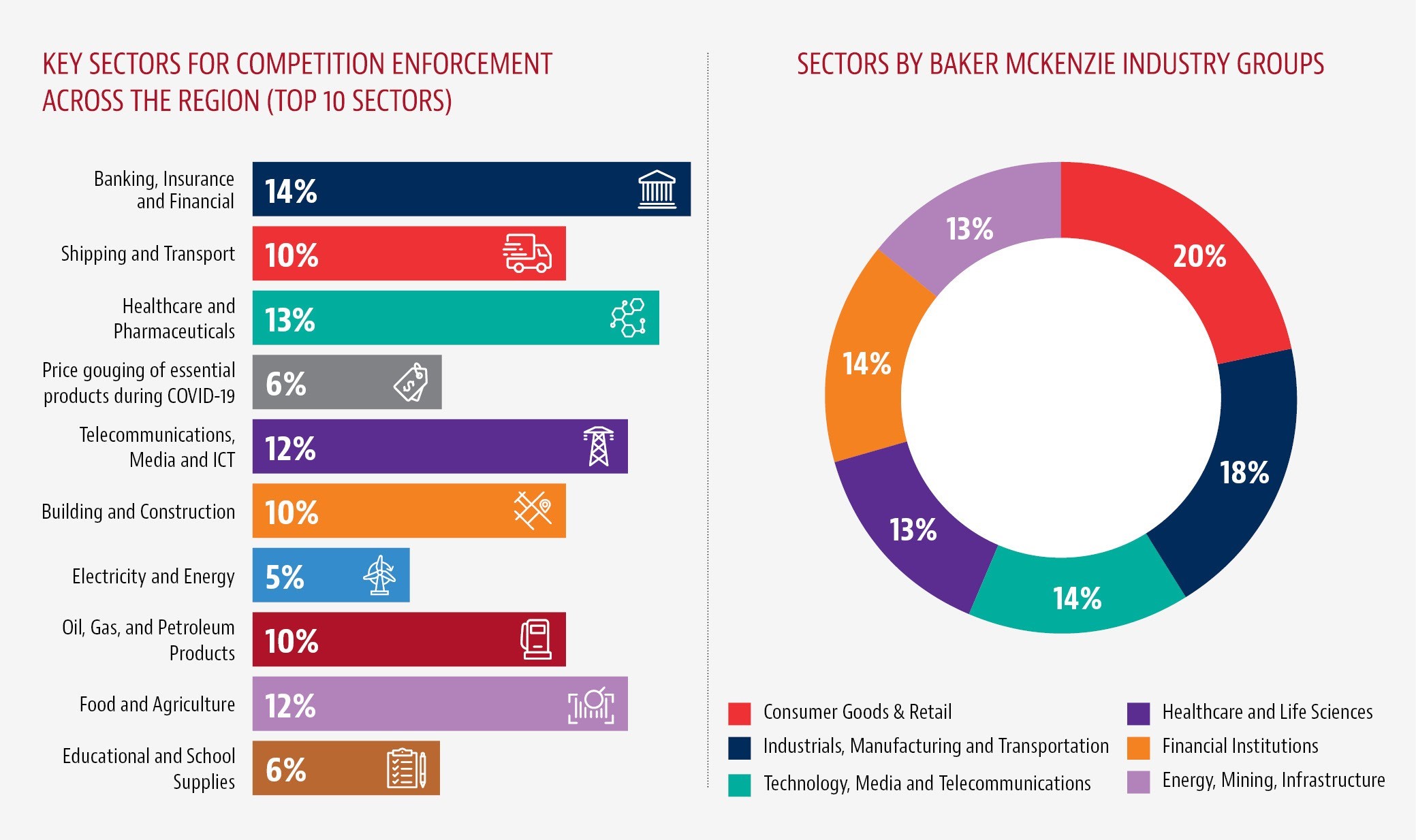
Collaboration efforts amongst competition authorities in the region
Various African competition authorities have signed Memoranda of Understanding (“MOU”) to foster cooperation in the enforcement of competition policy and law. Specifically, there exists MOU between the national competition authorities of the countries set out below:
- Angola – Portugal.
- Botswana – South Africa
- Eswatini – South Africa –Taiwan
- Kenya – South Africa
- Malawi – Tanzania – Zambia
- Mauritius – Seychelles – South Africa
- Namibia – South Africa
- Nigeria – United States
- South Africa – Mauritius – The Russian Federation – Brazil – Namibia – Eswatini – Kenya –Barbados – Botswana
- Zambia – Malawi – Zimbabwe – South Africa
- Zimbabwe – Zambia
Regional competition law bodies and instruments
Over the years, regional competition agreements (RCAs) have been adopted in Africa in terms of which regional competition bodies have been established to enforce competition provisions. These RCAs generally offer deeper levels of integration and a higher degree of co-operation on competition enforcement.
The table below reflects regional bodies and instruments and the national authorities’ memberships:
|
Jurisdiction |
Regional Competition Bodies / Instruments |
|||||||
|
COMESA1 |
EAC2 |
WAEMU3 |
SADC4 |
AfCFTA5 |
ACF6 |
ECOWAS7 |
CEMAC8 |
|
|
Algeria |
x | x | x | x | / | / | x | x |
|
Angola |
x | x | x | / | / | / | x | x |
|
Botswana |
x | x | x | / | / | / | x | x |
|
Cameroon |
x | x | x | x | / | / | x | / |
|
Cape Verde |
x | x | x | x | / | x | / | x |
|
Cote d’Ivoire |
x | x | / | x | / | / | / | x |
|
Egypt |
/ | x | x | x | / | / | x | x |
|
Eswatini |
/ | x | x | / | / | x | x | x |
|
Ethiopia |
/ | x | x | x | / | / | x | x |
|
Gabon |
x | x | x | x | / | / | x | / |
|
Ghana |
x | x | x | x | / | / | / | x |
|
Kenya |
x | x | x | x | / | x | / | x |
|
Madagascar |
/ | / | x | x | / | / | x | x |
|
Malawi |
/ | x | x | / | / | / | x | x |
|
Mali |
x | x | / | x | / | / | / | x |
|
Mauritius |
/ | x | x | / | / | / | x | x |
|
Morocco |
x | x | x | x | / | / | x | x |
|
Mozambique |
x | x | x | / | / | / | x | x |
|
Namibia |
x | x | x | / | / | / | x | x |
|
Nigeria |
x | x | x | x | / | / | / | x |
|
Rwanda |
/ | / | x | x | / | / | x | x |
|
Senegal |
x | x | / | x | / | / | / | x |
|
South Africa |
x | x | x | / | / | / | x | x |
|
Sudan |
/ | x | x | x | / | x | x | x |
|
Tanzania |
x | / | x | / | / | / | x | x |
|
Togo |
x | x | / | x | / | / | / | x |
|
Tunisia |
/ | x | x | x | / | / | x | x |
|
Uganda |
/ | / | x | x | / | x | x | x |
|
Zambia |
/ | x | x | / | / | / | x | x |
|
Zimbabwe |
/ | x | x | / | / | / | x | x |
1 Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA): the authority responsible for the implementation of the regional competition provisions in the common market for Eastern and Southern Africa. It conducts investigations of cross-border anti-competitive cases and reviews merger transactions, co-operating where necessary with the National Competition Authorities of the Member States.
2 East African Community (EAC): the EAC Competition Act gives the EAC Competition Authority exclusive original jurisdiction in the determination of violations of the EAC Competition Act, i.e. anti-competitive behaviour that has cross-border effect.
3 West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU): The WAEMU Competition Commission has exclusive jurisdiction over competition provisions in the union.
4 Southern African Development Community (SADC): is an inter-governmental organisation, which aims to further regional socio-economic cooperation and integration as well as political and security cooperation among 16 countries in southern Africa. SADC members signed and approved the Declaration on Competition and Consumer Policies in 2009 and cooperate on competition matters under various SADC committees / working groups.
5 African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA): on 1 January 2021, trading began in African countries that had ratified the AfCFTA agreement and submitted their tariff offers. All countries in Africa, except for Eritrea, have now signed the agreement and 41 countries have ratified it so far, including most of Africa’s major economies (South Africa, Kenya, Nigeria and Ghana, for example). Phase two of AfCFTA negotiations have begun, which include discussions on competition policy, investment protection and intellectual property rights, as well as deciding on the rules for governing trade on digital platforms. The intention is to conclude these negotiations by the end of 2022.
6 African Competition Forum (ACF): the ACF is an informal network of African national and multinational competition authorities. The principal objective of the ACF is to promote the adoption of competition principles in the implementation of national and regional economic policies of African countries.
7 Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS): is a regional political and economic of fifteen countries located in West Africa. The ECOWAS Regional Competition Authority is made responsible for enforcement of the regional competition provisions. It was established in 2008 but only launched on 12 July 2018 (hosted by Gambia).
8 Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC): the CEMAC Executive Secretariat is responsible for the implementation of the regional competition provisions in the Central African Economic and Monetary Community.
